Mitochondrial myopathy is a group of genetic diseases caused by defects in the way that mitochondria, or powerhouses in the cells, make energy for the body. The disorders affect the organs and tissues that use the most mitochondrial energy, such as the muscles, eyes, ears and central nervous system. Most mitochondrial myopathies occur before the age of 20, and often begin with exercise intolerance or muscle weakness. During physical activity, muscles may become easily fatigued or weak.
Prevalence: Mitochondrial disease cases is estimated to be 6.2–23.3 in 100,000 worldwide. These disorders affect both men and women, children and adults, and individuals of all ethnic and racial groups.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle disease
- Movement problems
- Diabetes
- Seizures
- Heart disease
- Fatigue
It is important to note that all of these symptoms do not affect everyone; they vary widely among individuals.
Role of Physiotherapy:
Exercise programs (either aerobic, endurance, or resistance) can provide a safe therapeutic option to patients with mitochondrial myopathy, benefiting the biochemical (increasing phosphocreatine synthesis and mitochondrial enzymes) and clinical (work capacity, fatigue, quality of life, and strength) end points.
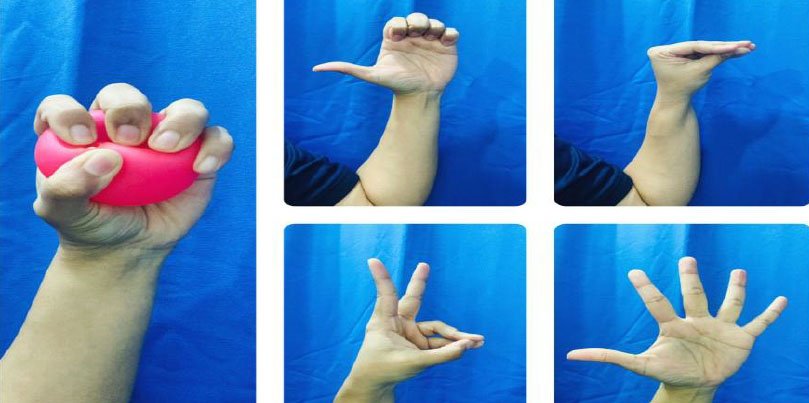
- Stretching exercises
- Strengthening exercises
- Balance training
- Endurance training
- Respiratory care
- Relaxation